Configuring Host
This page explains how to configure the information of a computational host.
How a job is submitted to a computational host
Generally speaking, we need to use a job scheduler, such as Torque, to submit a job to High-Performance Computers (HPCs) or CPU clusters. When submitting a job to a job scheduler, we usually need to specify various parameters such as the number of nodes required for the job, the maximum elapsed time, and the number of CPU cores.
The problem is that the specifications of these job schedulers are different from each other, showing a wide variety. Therefore, OACIS uses a small script, called XSUB to absorb the difference between schedulers. XSUB must be prepared in the computational hosts before you register the host information on OACIS.
About the installation procedure of XSUB, please refer to the readme of xsub or readme of xsub_py.
After you install either xsub or xsub_py properly, the commands xsub, xstat, and xdel became available.
(Note) OACIS runs these command from bash launched as a login-shell. Therefore, please set the environment variables required to use XSUB, such as PATH, in .bash_profile file, not in .bashrc.
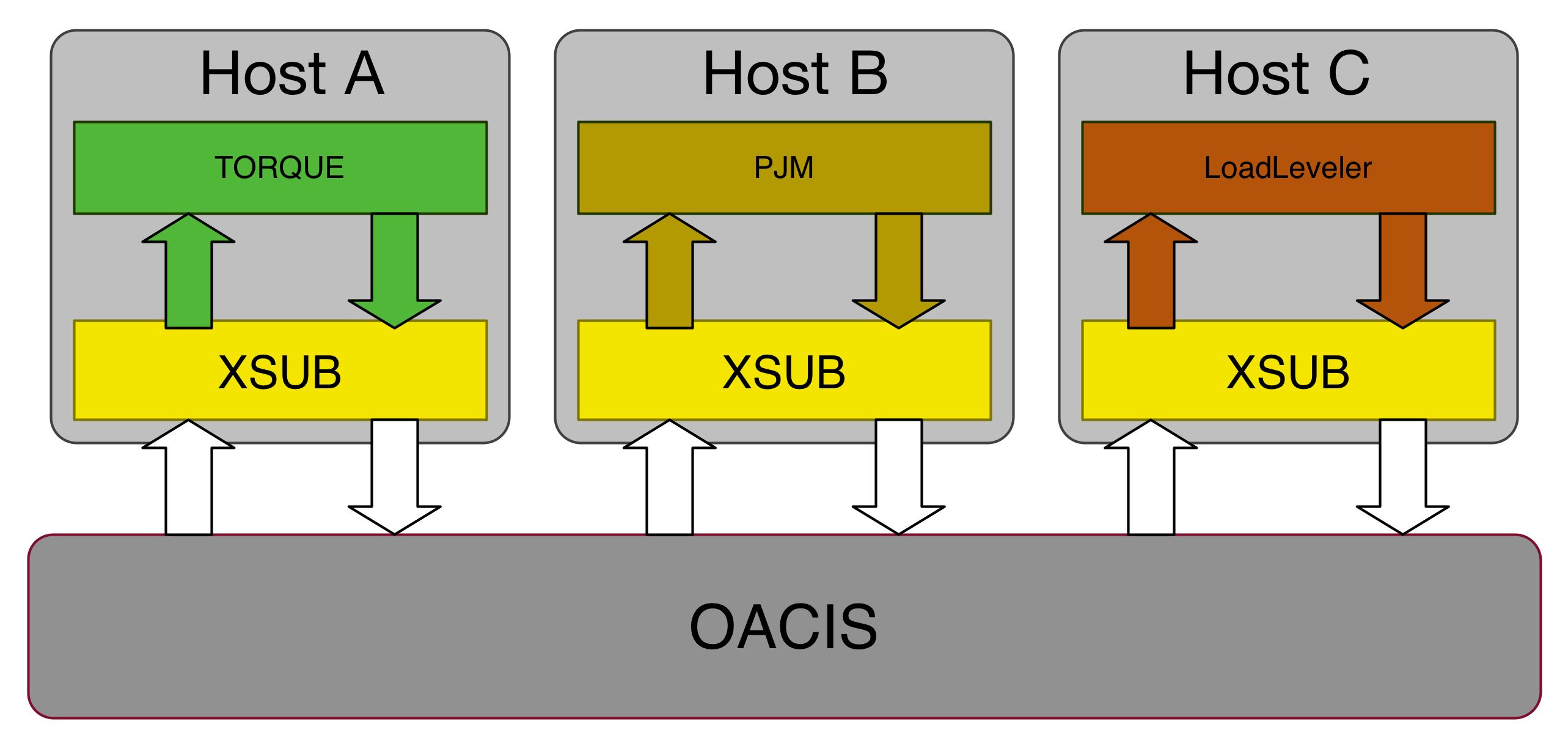
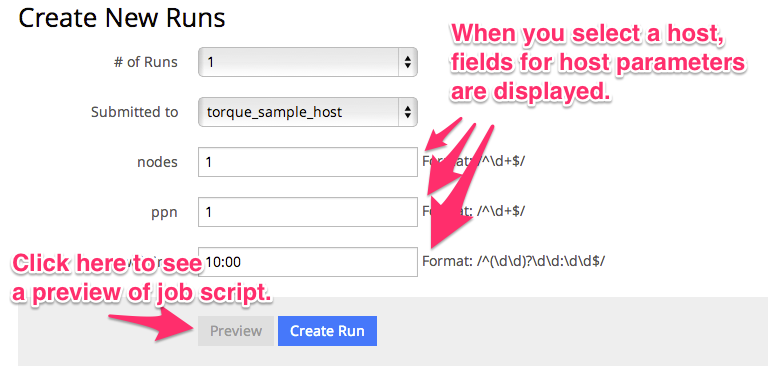
The parameters required to specify when submitting a job are called “host parameters”. Required host parameters are different depending on the specification of the job schedulers. OACIS retrieves the information of the required host parameters using the “xsub” command. Hence, XSUB must be setup before registering the host information on OACIS. When you create a run, fields for the host parameters are shown in the page as shown in the figure below.
Specification of Host
We will explain the list of information which you need to specify when registering a host.
| field | explanation |
|---|---|
| Name | The name used in “~/.ssh/config” file. |
| Work base dir | The path to the work directory. The work directory is the place where jobs are executed. Please specify the directory dedicated to OACIS jobs. |
| Mounted work base dir | If the work base dir is directly accessible from OACIS, specify the path which is accessible from OACIS. See the notes below this table. |
| Max num jobs | The maximum number of concurrent jobs. Jobs are queued until the number of running jobs becomes this number. |
| Polling interval | Time interval to check the status of the computational host. With this interval, SSH connection is made to check the status. The default value is 60 seconds. |
| MPI processes | The available range of the number of MPI processes. If you specify a number out of this range when making a run, you will get an error. |
| OMP threads | The available range of the number of OpenMP threads. |
| Executable simulators | List of executable simulators on that host. |
| Executable analyzers | List of executable analyzers on that host. |
| SSH Backend | The SSH implementation to use, either Net::SSH (Ruby) or PopenSSH (Shell). |
The SSH setting must be written in “~/.ssh/config” file. For instance, setting of “MyHost” may be written as the following.
Host MyHost
HostName example.com
User user_ABC
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
port 22
If you find an error like “no such command: xsub” when registering a host, please check if XSUB is properly installed.
[Advanced] Using the K-computer
In addition to the SSH and XSUB configurations, a special configuration is needed for the K-computer because of the staging functionality.
Since the executable file is also copied by staging, you can not specify the path to the executable by absolute path. The path changes after staging-in. Use “preprocess” to copy the executable to the current directory and specify the simulation command using the relative path from the current directory.
Suppose your executable file is located at ~/path/to/simulator.out. Please set the preprocess of the simulator as follows.
cp ~/path/to/simulator.out .
When you execute a job via xsub, the temporary directory prepared for the job is going to be staged-in. So, copy all the necessary files to the current directory in the pre-process.
Set the execution command as follows.
./simulator.out
By setting “command” and “pre-process” like these, we can submit jobs to the K-computer. All the simulation results are properly staged-out if all the output files are generated in the current directory because all the files in the current directory are staged-out.
Using SSH Multiplexing
SSH multiplexing allows re-use of the SSH connection after an initial login. The re-use of the connection means that you can log in one time, leave the connection open, and then connect again without having to reauthenticate. Therefore, you can authenticate using a password or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and then you can access the same system using OACIS without using your password or MFA token in OACIS.
In order to use the multiplexing, when creating your ~/.ssh/config file, add controlmaster auto and controlpath /tmp/ssh-%r@%h:%p. The configuration may be as the following:
Host MyHost
HostName example.com
User user_ABC
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
port 22
controlmaster auto
controlpath /tmp/ssh-%r@%h:%p
In the terminal, log in to the host using ssh MyHost.
In OACIS, select PopenSSH (Shell) for the SSH Backend, which will use OpenSSH, which includes ControlMaster, unlike Net::SSH (Ruby).
Then, OACIS should be connected to the host and be able to show the Host status and submit jobs.